


モバイルネットワーク技術情報
3GPP describes LTE radio access technology is described as follows:
The multiple access scheme for the LTE physical layer is based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) with a Cyclic Prefix (CP) in the downlink and a Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) with CP in the uplink.
OFDMA is particularly suited for frequency selective channel and high data rate. It transforms a wideband frequency selective channel into a set of parallel flat fading narrowband channels, thanks to the CP. This ideally allows the receiver to perform a low complexity equalization process in the frequency domain, i.e., 1 tap scalar equalization.
The baseband signal representing a downlink physical channel is defined in terms of the following steps, as shown in Figure 1:
Figure 1 : Overview of Downlink Physical Channel Processing.
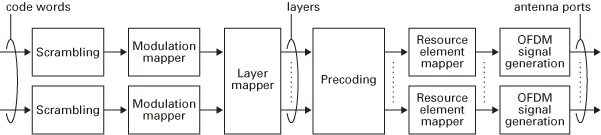
The baseband signal representing the physical uplink shared channel is defined in terms of the following steps, as shown in Figure 2:
Figure 2 : Overview of Uplink Physical Channel Processing.
