


モバイルネットワーク技術情報
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is the project name given to development of a high performance air interface for cellular mobile communication systems. It is the last step toward the 4th generation (4G) of radio technologies designed to increase the capacity and speed of mobile telephone networks. While the former generation of mobile telecommunication networks are collectively known as 2G or 3G, LTE is marketed as 4G.
According to 3GPP, a set of advanced requirements was identified:
Figure 1 : Roadmap to 4G
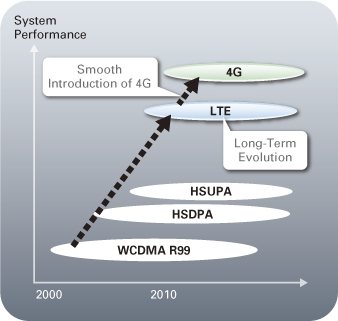
Although there are major changes between LTE and its 3G predecessors, it is nevertheless looked upon as an evolution of the UMTS / 3GPP 3G standards. LTE uses a different form of radio interface (OFDMA / SC-FDMA instead of CDMA), but there are many similarities with the earlier forms of 3G architecture and opportunities for re-use of some elements of 3G network architecture. LTE can be seen as providing an evolution of functionality, increased speeds and general improved performance compared to 3G.
LTE and 3G/3.5G Specification
(from NTT docomo Press Release)
| 3G WCDMA (R99) | 3.5G HSPA | LTE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Common frequency assigned for 3G | ||
| Bandwidth | 5MHz | 1.4/3/5/10/20 MHz | |
| Radio Access | DS-CDMA | DL: OFDMA | |
| UL: SC-FDMA | |||
| Uplink Peak Rate | 384kbps | 5.7Mbps | >50Mbps |
| Downlink Peak Rate | 384kbps | 14Mbps | >100Mbps |
| 3G WCDMA (R99) | 3.5G HSPA | LTE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Common frequency assigned for 3G | Common frequency assigned for 3G | Common frequency assigned for 3G |
| Bandwidth | 5MHz | 1.4/3/5/10/20 MHz | |
| Radio Access | DS-CDMA | DS-CDMA | DL: OFDMA |
| Radio Access | DS-CDMA | DS-CDMA | UL: SC-FDMA |
| Uplink Peak Rate | 384kbps | 5.7Mbps | >50Mbps |
| Downlink Peak Rate | 384kbps | 14Mbps | >100Mbps |
LTE has introduced a number of new technologies when compared to previous cellular systems. They enable LTE to operate more efficiently with respect to the use of spectrum, and also provide the much higher data rates that are now required.