モバイルネットワーク技術情報
- LTE-Advanced Tutorial
- What is LTE?
- What is LTE eNB?
- LTE eNB Evaluation
Methodology
- Abbreviations
RRC Protocol
According to 3GPP TS 36.331, the RRC protocol includes the following main functions:
- Broadcast of system information:
- NAS common information
- Information applicable for UEs in RRC_IDLE, e.g., cell (re-)selection parameters, neighboring cell information and information (also) applicable for UEs in RRC_CONNECTED, e.g., common channel configuration information.
- ETWS notification
- RRC connection control:
- Paging
- Establishment/modification/release of RRC connection, including assignment/modification of UE identity (C-RNTI), establishment/ modification/ release of SRB1 and SRB2, access class barring
- Initial security activation, i.e., initial configuration of AS integrity protection (SRBs) and AS ciphering (SRBs, DRBs)
- RRC connection mobility including intra-frequency and inter-frequency handover, associated security handling, i.e., key/ algorithm change, specification of RRC context information transferred between network nodes
- Establishment/ modification/ release of RBs carrying user data (DRBs)
- Radio configuration control including assignment/ modification of ARQ configuration, HARQ configuration, DRX configuration
- QoS control including assignment/ modification of semi-persistent scheduling (SPS) configuration information for DL and UL, assignment/ modification of parameters for UL rate control in the UE, i.e., allocation of a priority and a prioritized bit rate (PBR) for each RB
- Recovery from radio link failure
- Inter-RAT mobility including security activation, transfer of RRC context information
- Measurement configuration and reporting:
- Establishment/modification/release of measurements (e.g., intra-frequency, inter-frequency and inter- RAT measurements)
- Setup and release of measurement gaps
- Measurement reporting
- Other functions including transfer of dedicated NAS information and non-3GPP dedicated information, transfer of UE radio access capability information, support for E-UTRAN sharing (multiple PLMN identities)
- Generic protocol error handling
- Support of self-configuration and self-optimization
NOTE: Random access is specified entirely in the MAC including initial transmission power estimation.
Figure 1 : RRC States (from 3GPP TS 36.331)
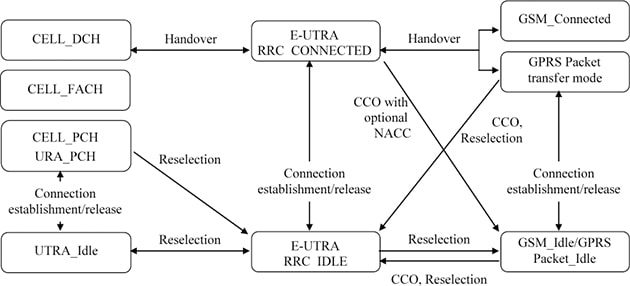
Signaling Radio Bearers (SRB) are defined as Radio bearers that are used only to transmit RRC and NAS messages. SRB’s are classified into three types:
Signaling Radio Bearer 0 (SRB0): RRC message using CCCH logical channel.
Signaling Radio Bearer 1 (SRB1): is for transmitting NAS messages over DCCH logical channel.
Signaling Radio Bearer 2 (SRB2): is for high priority RRC messages. Transmitted over DCCH logical channel.



